Some people say that there is no difference in hardware between straight stroke and angle stroke. It is just a parameter inside, and there is no need to have a separate option when selecting a model. Some people say that now are not all intelligent? Why does the positioner still distinguish between straight and angular travel?
The view that there is no difference between the two is wrong, the valve positioner has a straight stroke and angular stroke points.
This topic can be divided into 2 directions, that is, the difference between intelligent positioner and mechanical positioner!
A. Mechanical positioner
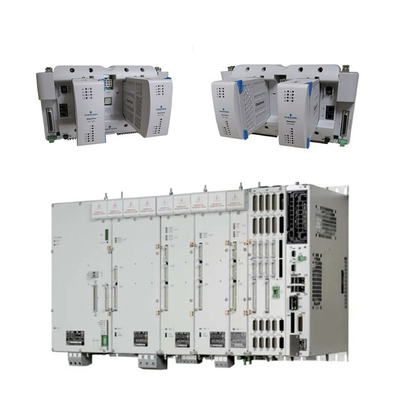
Traditional mechanical positioner, YT-1000 positioner as an example, is a typical mechanical positioner, affordable and durable, loved by users.

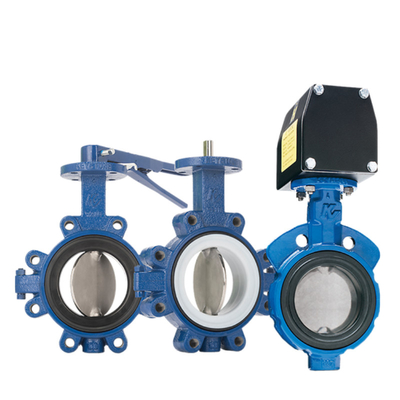
In the selection, according to the valve's trajectory to distinguish, up and down straight line movement with straight stroke, 90 degree rotation with angular stroke, another selection sample inside the detailed instructions:

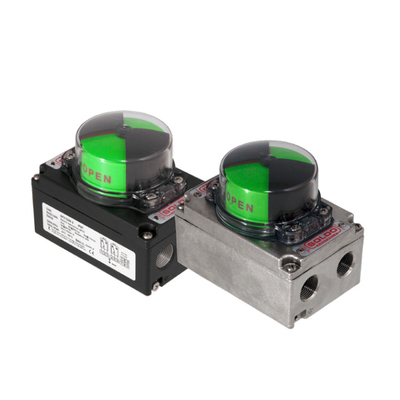
B. Intelligent positioner
Intelligent positioner itself straight stroke and angle stroke is no distinction, just inside the debugging parameters have changed, mainly due to its intelligent design, adaptive features and parameterized configuration capabilities. The following are specific reasons for analysis:
1. Hardware versatility and software adaptation
Intelligent positioner using modular design, the same hardware platform can be configured through the software to support a variety of travel types. For example:
- Signal processing compatibility: Whether it is linear displacement or angular rotation, the intelligent positioner can unify the physical movement into a standard electrical signal (e.g., 4~20mA), and process the difference through internal algorithms.
- Parameterized switching: The user selects “straight travel" or “angular travel" mode through menu settings (e.g. P1.0 configuration menu of ABB smart positioners) without changing hardware. For example, ABB intelligent positioner needs to choose the operation mode according to the actual installation form during commissioning, and the system automatically calls the corresponding linearization calibration database.
2. Adaptive calibration and automatic adjustment
The core advantage of the intelligent positioner lies in its adaptive calibration function, which can automatically identify and adapt to different stroke types:
- Auto-calibration program: After starting auto-tuning (e.g. ADJ-LIN or ADJ-ROT mode of ABB smart positioner), the smart positioner will drive the actuator to full travel motion, record the displacement or angle range, and generate the optimal control parameters. This process eliminates the need to manually differentiate between travel types and simply ensures that the mounting form matches the menu selection.
- Dynamic compensation ability: real-time monitoring of the valve position through the built-in sensors, combined with the PID algorithm to dynamically correct the non-linear error (such as the arc-shaped movement trajectory of the angular stroke and the linear displacement difference between the straight stroke).
3. Standardized interface and signal unification
Signal standardization: No matter straight stroke or angle stroke, the input/output signals of the intelligent positioner follow the unified standard (e.g. 4~20mA, HART protocol), which can be seamlessly connected with the control system. For example, Siemens intelligent positioners are adapted to different valve types through a unified interface, and you only need to specify the type of travel in the configuration.
Position feedback generalization: Using non-contact sensors (e.g. magneto-resistive or photoelectric encoders), linear displacement or rotational angle can be measured directly and converted into uniform position percentage feedback through algorithms.
4. Flexibility of application scenarios
- Multi-valve compatibility: the same intelligent positioner can be adapted to different valve types (such as ball valves, butterfly valves, regulating valves), only need to adjust the parameters. For example, when the smart positioner switches between a ball valve (angle stroke) and a control valve (straight stroke), it only needs to re-run the auto-calibration program without replacing the device.
- Reduced maintenance complexity: companies do not need to stock multiple intelligent positioners for different valves, reducing inventory costs and maintenance training needs.
5. Technology Development Trends
- Intelligent integration: modern intelligent positioner integrated microprocessor and AI algorithms, can learn the characteristics of the valve and dynamically optimize the control parameters, and further blur the boundaries of straight and angular travel.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) support: through remote configuration and cloud parameter library, intelligent positioner can automatically download the configuration file adapted to different strokes, realizing “plug and play".
Through the three core capabilities of hardware generalization, software parameterization and adaptive calibration, the intelligent positioner realizes the unified support for straight and angular travel. Its essence is to abstract the physical differences into configurable parameters through intelligent technology, so as to simplify the process of installation, commissioning and maintenance, and to enhance the flexibility and reliability of industrial automation systems.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 







