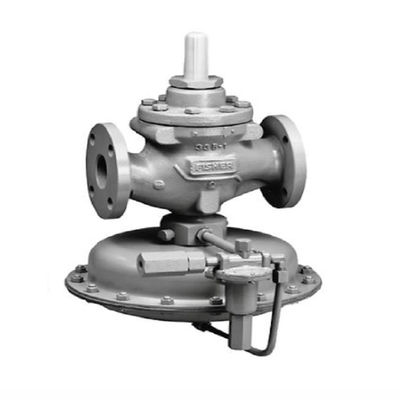
I. Brief introduction of control valve
Control valves are usually composed of electric actuator or pneumatic actuator and valve body. Straight stroke mainly through the single-seat type and through the double-seat type two, the latter has a large flow capacity, the unbalance force is small and stable operation, so usually especially suitable for large flow, high pressure drop and leakage less occasions. Angle stroke are: V-type electric regulator ball valve, pneumatic membrane cut-off valve, eccentric butterfly valve and so on.
II. Principle of operation
When the air chamber input 0.02 ~ 0.10Mpa or 0.08 ~ 0.24Mpa signal pressure, the film produces thrust, so that the thrust disk moves downward, compressing the spring, driving the push rod, stem, spool downward movement, the spool left the valve seat, so that the compressed air circulation. When the signal pressure is maintained at a certain level, the valve is maintained at a certain opening.
1. Composition of the regulating valve:
By the actuator and valve body two parts. Among them, the actuator is the valve's driving device, which according to the size of the signal pressure to produce the corresponding thrust, so that the push rod to produce the corresponding displacement, thus driving the spool action of the valve.
2. Pneumatic actuator characteristics:
Pneumatic thin-film actuator features, simple structure, reliable action, easy maintenance, low price, is a kind of the most widely used actuators. Pneumatic thin-film actuator is one of the most commonly used actuators, its traditional mechanism is shown in the figure below.

3. Principle of action
Positive action: from the upper membrane cover of the air source interface to the membrane cover and membrane membrane chamber composed of air, the air pressure on the diaphragm and tray, compression of the spring, to overcome the spring force downward movement, but also drive the actuator downward movement. Afterwards, if the air pressure inside the membrane chamber decreases, the return force of the spring moves the diaphragm, the tray and the actuator upwards.
Reaction: Air is fed into the membrane chamber composed of the membrane cover and the membrane sheet from the air supply port of the lower membrane cover. The air pressure acts on the membrane sheet and the tray, compresses the spring, overcomes the spring force to move upward, and also drives the actuator to move upward.
There are two types of valves, positive and negative, when the spool moves downward, the flow area between the spool and the valve seat decreases, which is called positive; on the contrary, it is called negative. Gas-open control valve with the valve signal pressure increases the circulation area also increases; gas shut-off type is the opposite, with the increase in signal pressure and circulation cross-sectional area decreases.
III. Classification of control valves
According to the use and role, the main parameters, pressure, medium operating temperature, special purpose (i.e., special, special valves), drive energy, structure and other ways of categorization, of which the most commonly used classification is the structure of the regulating valve is divided into nine categories, six kinds of straight stroke, three kinds of angular stroke.
This classification method both by principle, role and structure, is currently the most commonly used domestic and international classification method. Generally divided into nine categories:
- single-seat control valve;
- Double-seated adjustment valve;
- sleeve control valve;
- Angle-shaped control valve;
- Three-way control valve;
- Diaphragm valve;
- Butterfly valve;
- Ball valves;
- Eccentric rotary valves. The first six are straight stroke and the last three are angle stroke.
IV, the flow characteristics of the control valve
Control valve flow characteristics Control valve flow characteristics, is a valve at both ends of the differential pressure to maintain a constant condition, the relative flow of media flow through the control valve and its relationship between the degree of opening. The flow characteristics of the control valve have linear characteristics, equal percentage characteristics and parabolic characteristics of three. The significance of three kinds of injection characteristics are as follows:
-
equal percentage characteristics (logarithmic)
Equal percentage characteristics of the relative stroke and relative flow is not a linear relationship, at each point in the stroke of the unit stroke changes caused by changes in the flow rate is proportional to the flow rate of this point, the flow rate of change in percentage is equal. So its advantage is that when the flow rate is small, the flow rate change is small, when the flow rate is large, then the flow rate change is large, that is, in different degrees of opening, with the same accuracy of regulation.
-
linear characteristics (linear)
Linear characteristics of the relative stroke and relative flow into a straight line relationship. Changes in the unit stroke caused by changes in the flow rate is unchanged. When the flow rate is large, the flow rate relative value changes are small, when the flow rate is small, the flow rate relative value changes are large.
-
parabolic characteristic
Flow rate according to the stroke of the two sides of the proportional change, roughly linear and equal percentage characteristics of the intermediate characteristics.
From the analysis of the above three characteristics can be seen, in terms of its regulatory performance, equal percentage characteristics for the optimal, stable regulation, good regulatory performance. And parabolic characteristics and better than the linear characteristics of the regulatory performance, according to the requirements of the use of different occasions, select any one of the flow characteristics.
V. Inspection and maintenance safety precautions
- the correct use of working conditions, the gas source is dry, no oil, no dust, keep clean.
- the medium temperature in line with the conditions of use of the valve.
- Correctly select the flow direction, calibrate the pressure difference before and after.
- instrumentation personnel must be agreed by the operator for the relevant ticket before maintenance, calibration of the control valve.
- the use of the valve body needs to be dismantled, before and after the cut-off valve must be confirmed by the operator to cut dead before dismantling.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 







